| TUD Organische Chemie | Immel | Tutorials | Symmetry | Three-dimensional Stereographs | View or Print (this frame only) |
Three-dimensional Stereographs and Symmetry Elements:
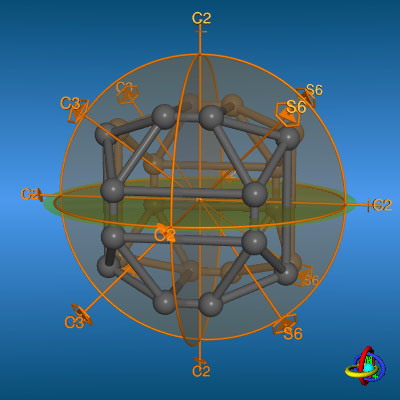
The table below provides an overview on the three-dimensional stereographic representations of point groups (including the 32 'Crystallographic Point Groups'). Please note, that although any positive integral value of n is allowed for the Cn, Cnv, Cnh, Dn, Dnh, Dnd, and Sn point groups of molecules, only a limited number is listed here. Additionally, the S1 point group is equivalent to Cs and S2 corresponds to Ci, any Sn with odd values of n is categorized under Cnh and thus not considered here. Chiral point groups are marked by bold-face point group symbols, all other point groups are achiral. The order of each point group is indicated in parenthesis, it is equivalent to the number of symmetry related positions in the stereographic projections. The point group Kh of a sphere was included for completeness, no molecule belongs to this group.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This table lists the symmetry elements of point groups including the order of the group
(i.e. the number of symmetry related positions in the stereographic projections).
See also the 'Hierarchy of Point Groups - Symmetry Correlations'.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||